By Pam Floyd, Mother and Fed is Best Advocate
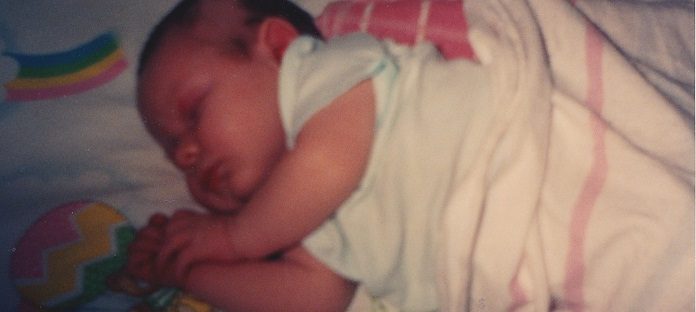
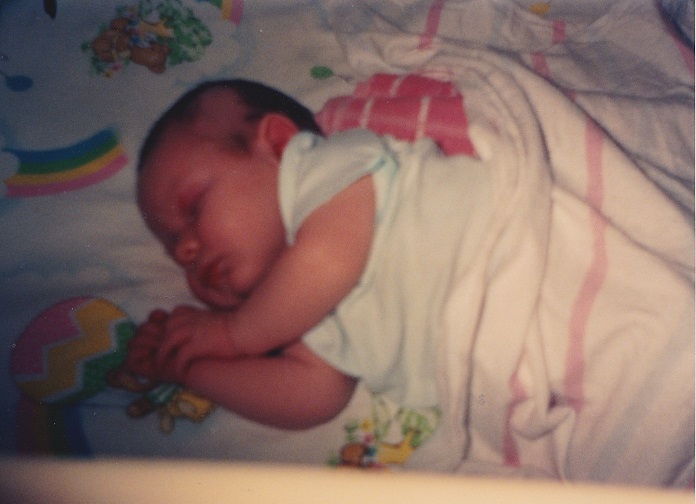
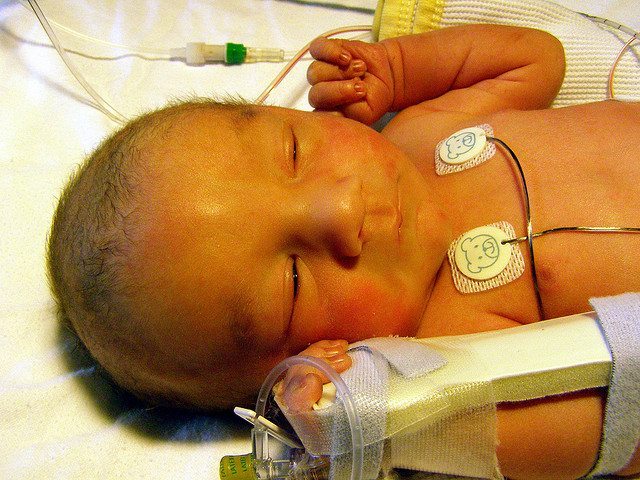
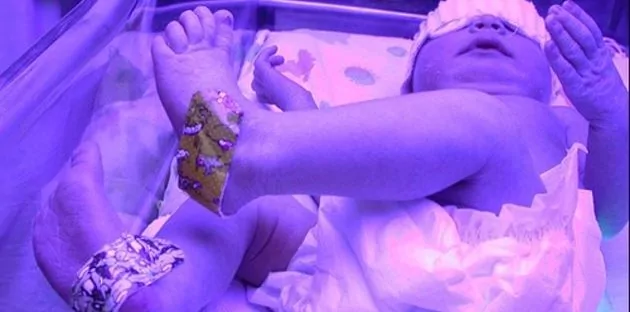
Twenty-five years ago, Chaz, the son of Pam Floyd, was born and developed hypernatremic dehydration from insufficient breast milk intake while exclusively breastfeeding. Chaz developed brain injury from dehydration and now lives disabled with cerebral palsy. Their story was published on the front page of the Wall Street Journal. She was subsequently interviewed on 20/20, which prompted a similar feature on ABC’s Prime Time Live. Pam contacted the Fed is Best Foundation to share her story again to warn mothers of the dangers of insufficient feeding.
“25 Year Anniversaries Should Be Celebrated Not Served As A Warning”
Twenty-five years ago my son almost died. He was only six days old. I had chosen to breastfeed, as everyone around me kept reminding me that ‘breast is best.’ So I followed their advice, and I exclusively breastfed. Even though I felt like something wasn’t quite right those first few days, everyone assured me everything was fine. The nurses in the maternity ward suggested that since I was a new mother, I wasn’t able to appreciate how much he was getting. The home health nurse that visited me, courtesy of my health insurance, the day after I left the hospital, reassured me that as long as he was getting six to seven wet diapers a day, then he was getting enough. And the nurses in my pediatrician’s office told me not to worry, that he was a big baby that he would eat when he got hungry. And my personal favorite, “the great thing about breast milk is that you never have to worry about how much or how little he’s getting. Because he’ll always get what he needs.” Well, that works great, if your milk comes in. My colostrum wasn’t enough for my son, Chaz. And my body never produced enough milk to keep a 10 lb. 4 oz. baby boy healthy.
Then when my son’s eyes started rapidly zig-zagging back and forth on that sixth day of life and I called the pediatrician’s office to tell them he was having a seizure, they told me that I didn’t know what I was talking about and that sometimes newborn’s eyes do that as they often wander. Well, the pediatrician finally agreed to see us. We were immediately sent to the emergency room. Then we were transferred to the children’s hospital. There, my son was put into a drug-induced coma until his seizures were under control. His diagnosis was a stroke due to hypernatremic dehydration. Children’s Hospital had me use their hospital grade breast pumps those first few days. The most I ever pumped was 3 cc’s. About a teaspoon. Usually, I just came back with mist. Or what looked like spit. There was never milk. I never got engorged. I never leaked. There was never any milk.
I got mad about this. Especially when I found out that it can and does happen regularly. It didn’t show up in any of my baby books or videos. So I called our local newspaper, The Virginian Pilot, and asked them to write an article about it, they did, it was called, “Mother Knows Best.” That was later revived by a journalist from The Wall Street Journal in an article entitled, “Dying for Milk: Some Mothers, Trying In Vain to Breast-Feed, Starve Their Infants — `Yuppie Syndrome’ Among Well-Meaning Parents Stems From Bad Advice — A Generation of Perfectionists.” We made the front page with that one. Of course, that set off a media frenzy.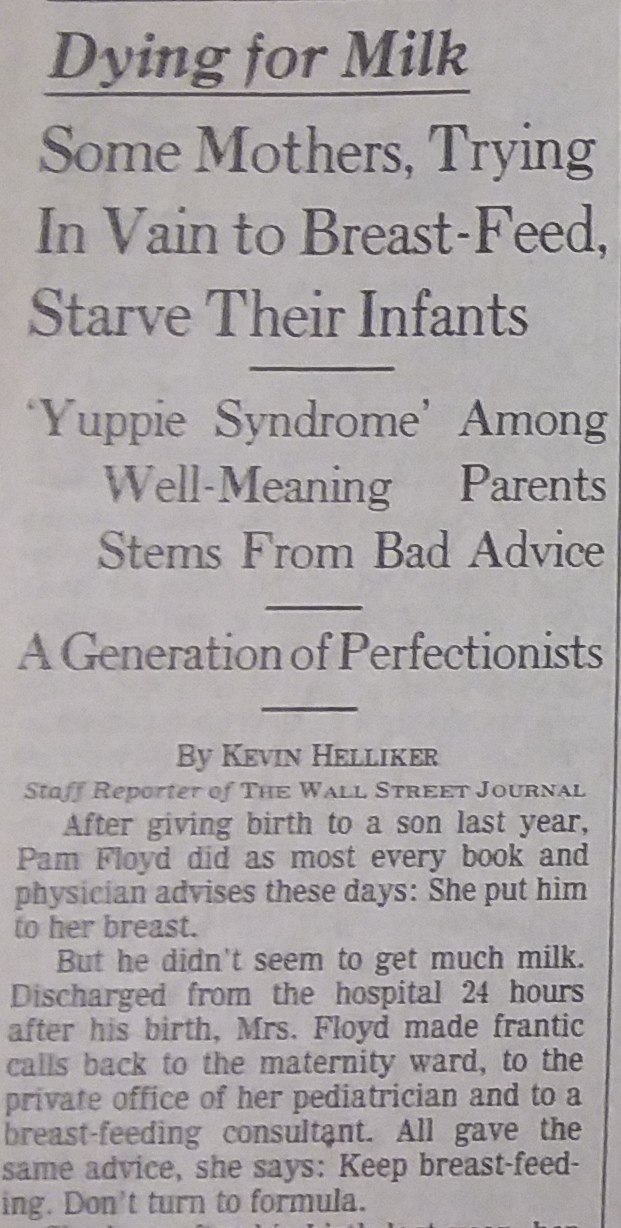
Continue reading