Updated February 1, 2024
We are proud to present the latest edition of the Fed is Best Guide to Safe and Optimal Infant Feeding. The feeding plan helps you decide and communicate how you would like to feed your newborn infant after birth and what you would like to do in case feeding problems and need for supplementation occur. This is for all families regardless of how they want to feed their baby, whether they are exclusively breastfeeding, supplemented breastfeeding as needed, or exclusive formula-feeding. Included in the plan are helpful resources, an informed consent form, and a comprehensive feeding log for your first days of feeding your baby:
Click here or the picture below for the Fed Is Best Guide To Safe and Optimal Infant Feeding:
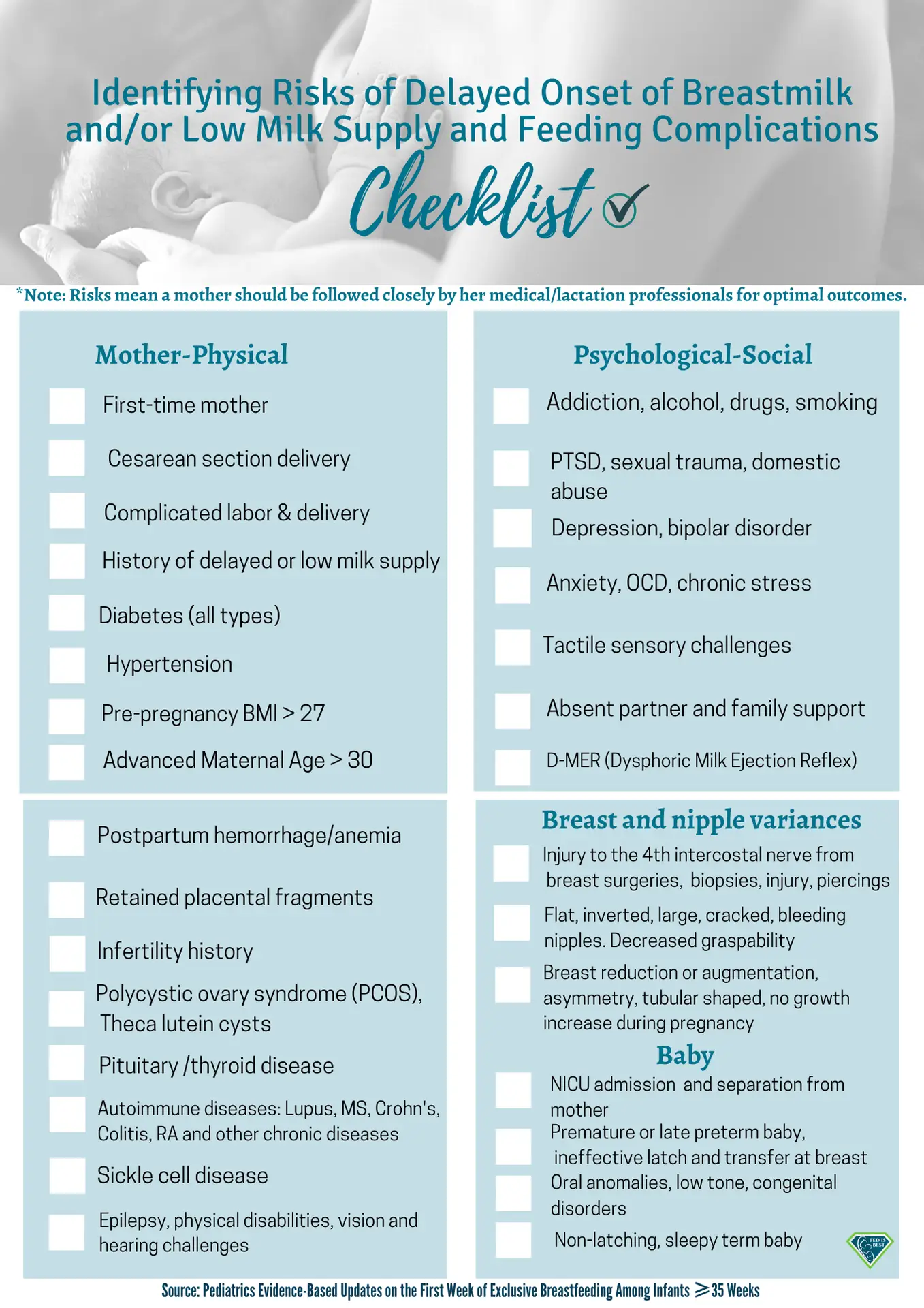
Checklist for risk factors associated with feeding complications and jaundice
Signs of a HUNGRY newborn

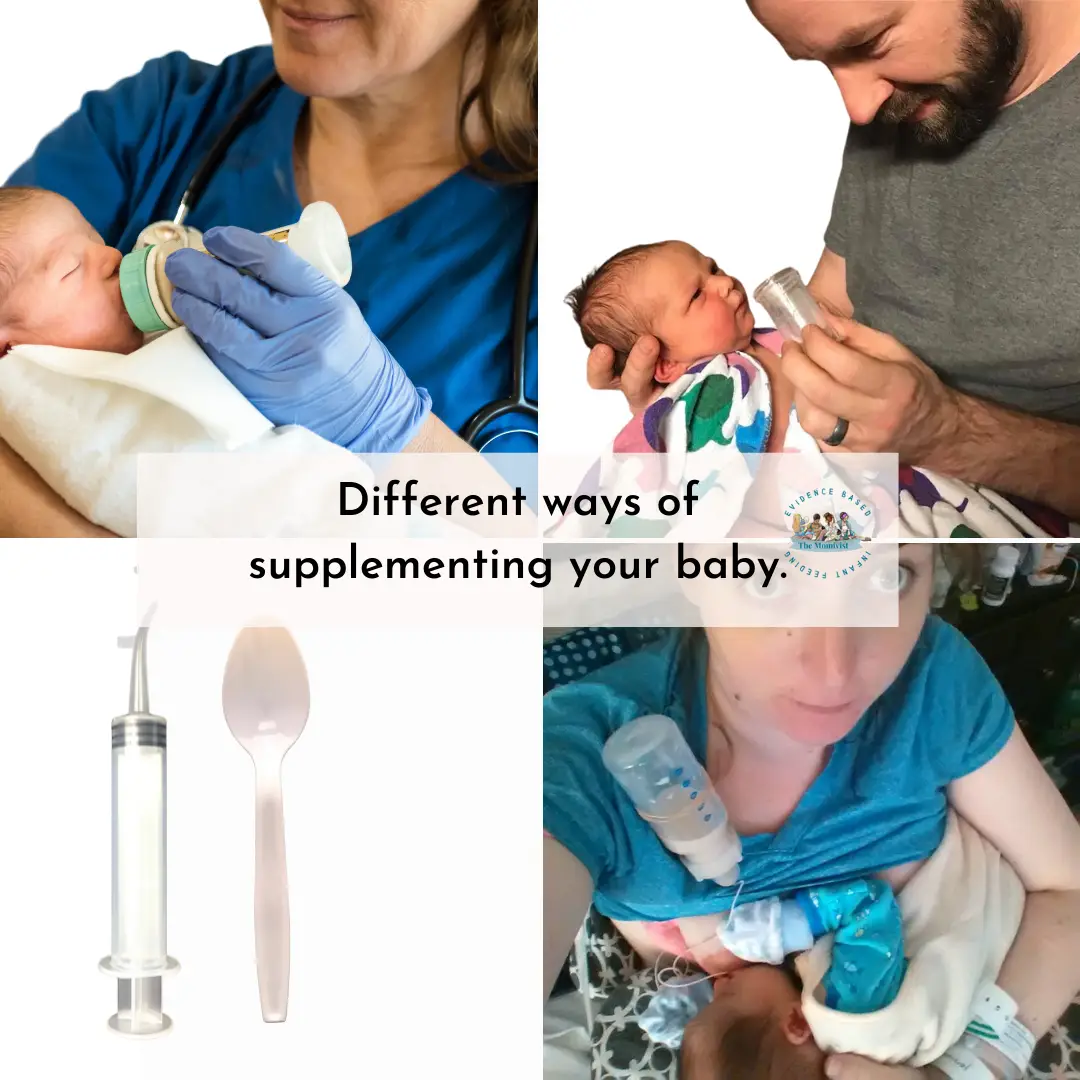
Fed Is Best Guide to Supplementing a Breastfed newborn
Click here for how to supplement your baby while maintaining breast stimulation until the arrival of your full milk supply
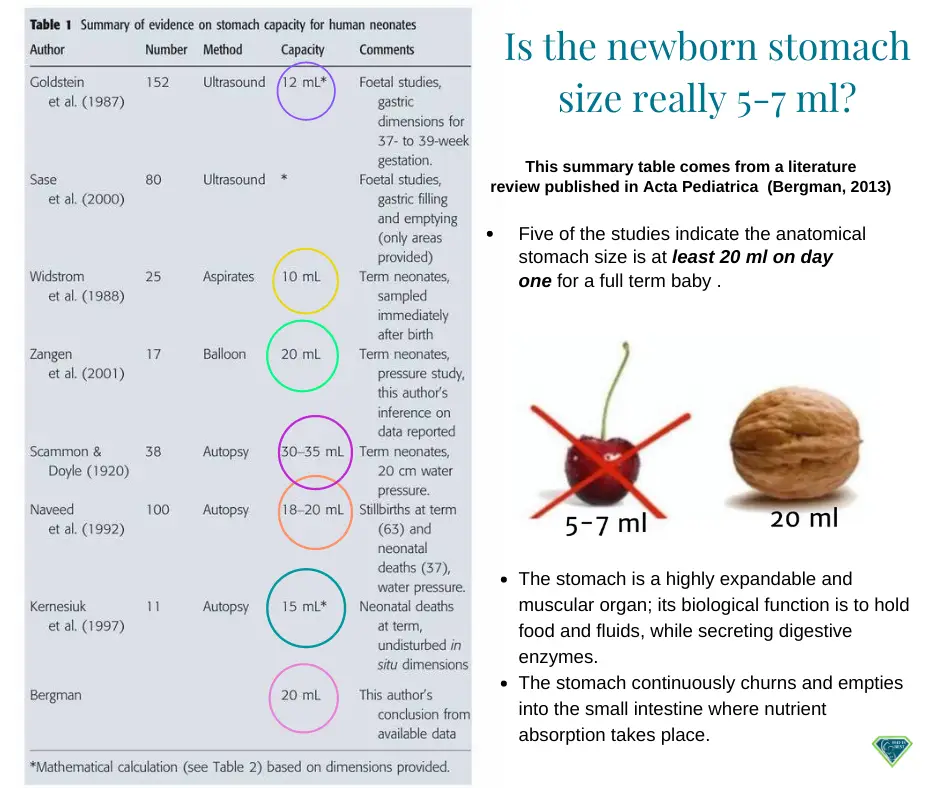
Information on the correct newborn stomach size
Other Important Resources
I Supplemented My Baby Until My Milk Came In And We Are Still Breastfeeding At 3 Months
How To Prepare For Supplementing When Breastfeeding Your Baby In The Hospital
We believe all babies deserve to be protected from hunger and thirst every single day of their life and we believe that education on safe infant feeding should be free. If you would like to make a donation to support the Fed is Best Foundation’s mission to teach every parent Safe Infant Feeding, please consider making a one-time or recurring donation to our organization.
Disclaimer: This document does not replace in-person physician evaluation and treatment. This document is meant to inform parents of the most recent data regarding infant feeding and to increase their knowledge on how to protect their newborns from hyperbilirubinemia, dehydration, hypernatremia, hypoglycemia and extended or repeat hospitalizations due to complications from underfeeding. Earlier supplementation may be needed for babies who are premature or have medical conditions. It is recommended that a parent seeks evaluation by a pediatrician for any concerns regarding the health and safety of her baby if they arise.

