Christie del Castillo-Hegyi, M.D.
From December 2018 to January 2019, the Secretary’s Advisory Committee on National Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Objectives for 2030 published the proposed Healthy People 2030 Objectives for public comment. Of note, the proposed Healthy People 2030 objectives saw a marked change from the 2020 objectives, namely a reduction of the breastfeeding objectives from 8 goals to one, namely, “Increase the proportion of infants who are breastfed exclusively through 6 months” (MICH-2030-15 ). Among the objectives that were dropped from the list were:
- MICH-23 – Reduce the proportion of breastfed newborns who receive formula supplementation within the first 2 days of life.
- MICH-24 – Increase the proportion of live births that occur in facilities that provide recommended care (i.e. Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative-certified hospitals) for lactating mothers and their babies.
| Healthy People 2020 Objectives | Baseline (%) | Target (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Increase the proportion of infants who are breastfed (MICH 21) | ||
| Ever | 74.0* | 81.9 |
| At 6 months | 43.5* | 60.6 |
| At 1 year | 22.7* | 34.1 |
| Exclusively through 3 months | 33.6* | 46.2 |
| Exclusively through 6 months | 14.1* | 25.5 |
| Increase the proportion of employers that have worksite lactation support programs (MICH 22) | 25† | 38 |
| Reduce the proportion of breastfed newborns who receive formula supplementation within the first 2 days of life (MICH 23) | 24.2* | 14.2 |
| Increase the proportion of live births that occur in facilities that provide recommended care for lactating mothers and their babies (MICH 24) | 2.9‡ | 8.1 |
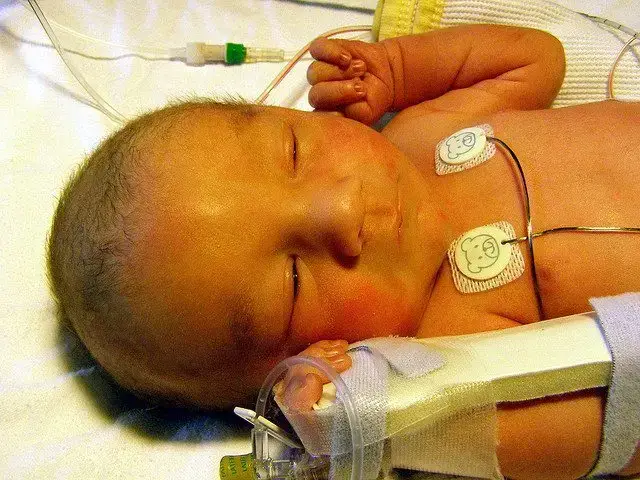
Exclusive breastfeeding at discharge is a major risk factor for severe jaundice and dehydration. Both conditions can require in-hospital treatment and can result in permanently impaired brain development. Photo Credit: Cerebral Palsy Law