Written by Jody Segrave-Daly, MS, RN, IBCLC
As a NICU/nursery nurse and IBCLC who has worked with newborn babies my entire nursing career, I was mystified when I first heard the phrase “second-night syndrome.” When I began to research where the phrase came from, it became clear that it is not based on any scientific research but rather on a theory that describes the behavior of exclusively breastfed newborns on their second day of life. It’s a frightening phrase for new parents to hear, as “syndrome” is definedas a group of signs and symptoms that characterize a particular abnormality or condition.
What is Normal Newborn Behavior
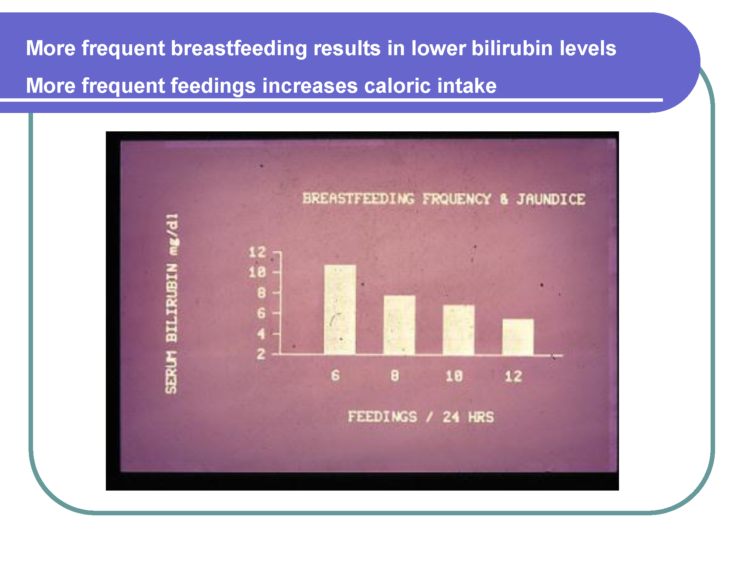
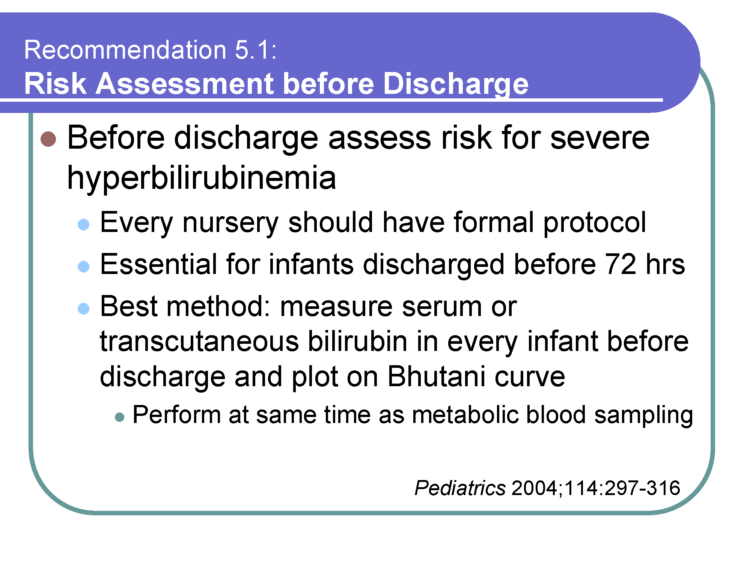
Babies go into a very deep recovery sleep period after the first 2 hours from birth. This period can range from 8-12 hours after birth and is often a time that babies may not wake up on their own to feed every 2-3 hours. Babies often need encouragement from their parents to wake them up for feeding sessions. Some babies are so sleepy that they nurse for 5 minutes or suckle on a bottle for 5 minutes or less and fall back asleep. It’s well known that babies fast during this time, and if they have enough caloric reserves, they may tolerate this fasting period without complications.
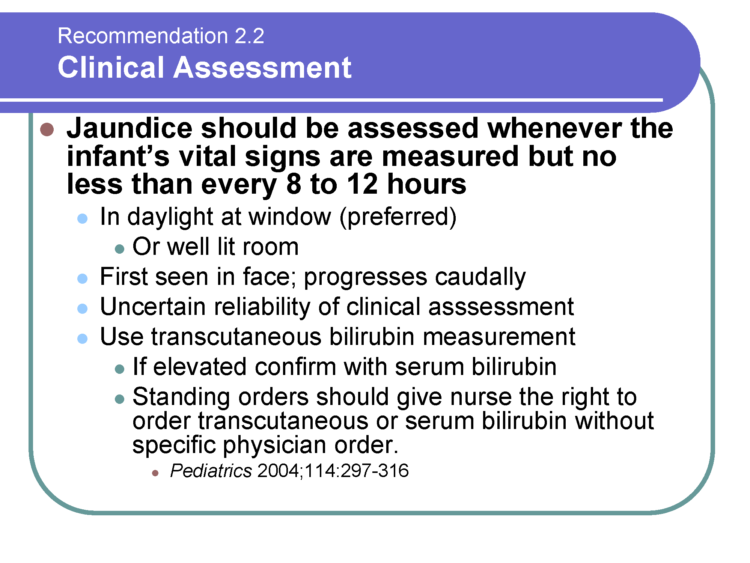
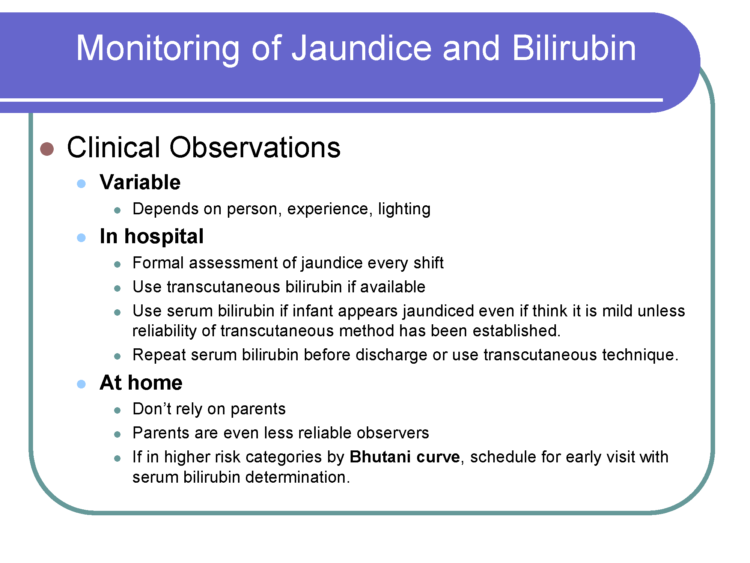
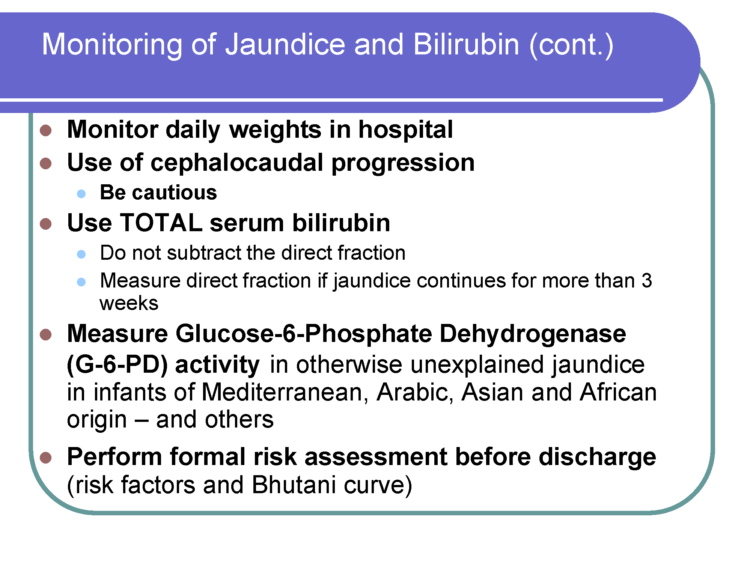
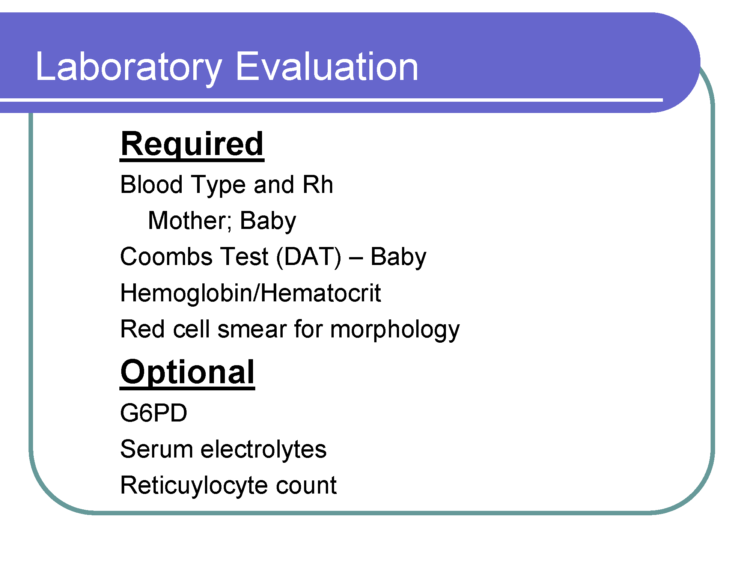
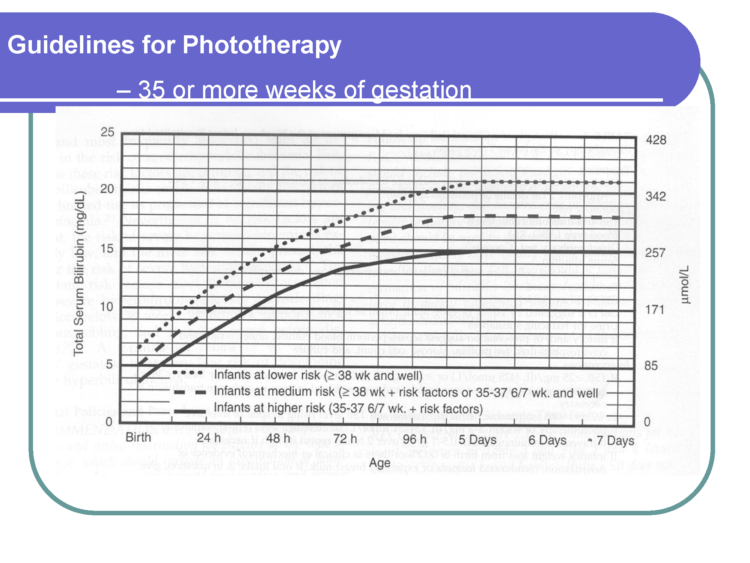
Nursery nurses are skilled in performing clinical assessments of babies to ensure they are stable. They are looking for signs of hypoglycemia or low blood sugar levels, jaundice, and other abnormal clinical markers.Ten percentof healthy, full-term, exclusively breastfed newborns develop hypoglycemia in the first days of life and may require specialized care until they are stable. Hypoglycemia has serious complications if uncorrected with supplementation. All babies transition from intrauterine to extra-uterine life and require skilled nurse observation.

After babies begin to ‘wake-up’ from their deep recovery sleep period on their second day of life, they will exhibit stronger hunger cues to nurse or bottle-feed every 2-3 hours and become much more alert. This is a new opportunity for parents to bond because their babies become alert again, opening their eyes while gazing at their parent’s adoring faces. Some babies are very demanding during this time because they are hungry.
Newborn babies are very easy to console after their feeding by being held and snuggled. Every nursery nurse will tell you something is wrong if a baby is not content after feeding. I suspect this is where the word “syndrome” came from, which describes abnormal infant behavior.
What does the newborn feeding pattern look like?
Breastfeeding: Every 2-3 hours, a baby will nurse for at least 15 minutes on each breast. Breastfeeding every 2-3 hours also stimulates the milk-making hormone cascade, which brings in a mother’s milk in 2-3 days. If your sleepy baby is not nursing effectively, self-expression of colostrum or pumping is necessary. Feed your baby with your expressed colostrum.
Supplementing is necessary if you are not producing enough because drops of colostrum are not enough to sustain your baby’s hunger and thirst. Check our resources on breastfeeding latch,safe positioning while breastfeeding, and how to supplement your baby while protecting your milk supply.
Bottle and formula feeding: Sometimes, bottle feeding will take about half as much time as breastfeeding, but similar feeding patterns occur because of the same caloric needs and thesame infant stomach size, which is roughly 20 -30 mL.
- Term newborns weighing over 6 pounds will feed for the first three days of life, nearly every 3 hours.
- Term newborns who weigh less than 6 pounds will feed the first three days of life every 2-3 hours.
- After three days, feed on demand according to your pediatrician’s guidelines.
- A newborn should not go greater than 4 hours without a successful and satisfactory feeding, especially in the first days of life.
How Much Milk Does My Baby Need?
- 1-24 hours old: 15-30 mL
- 24-48 hours old: 20-40 mL
- 48-72 hours old: 25-50 mL
These are approximate volumes as some babies may take more milk per feeding depending on the fuel reserve they are born with, their weight, their gestational age, and many other variables. For example, a 9-pound baby may want to take 45 ml at each or some feedings. If they do take more, that is okay. A 24-hour volume intake is the most important consideration, as babies can vary from feed to feed, as exhibited by their hunger cues.

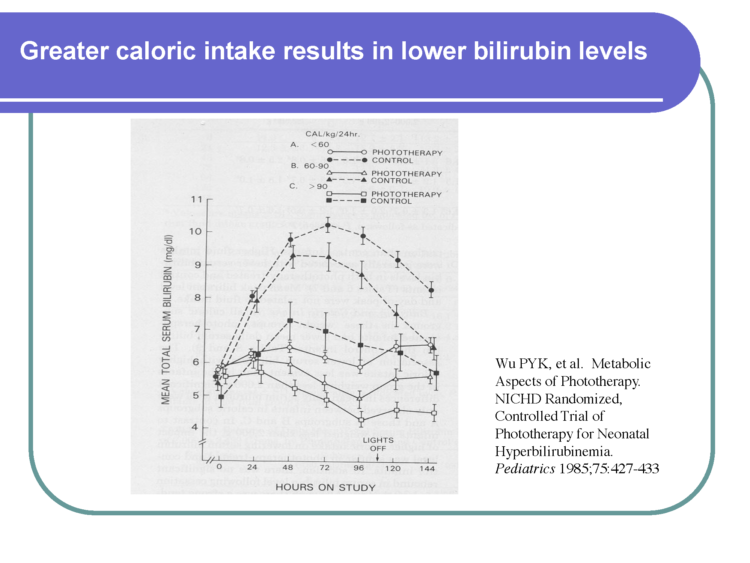
Colostrum has fewer calories(3 calories/5 ml) than mature human milk (5 calories/5 ml).

But what about the newborn stomach size?
The newborn stomach size is 4-5 times larger than the parents are being told. Why? To prevent babies from being supplemented is my first guess.
What does the research say about the newborn stomach size?

Some breastfeeding mothers talk about the “second-night syndrome” by describing itas absolute hell! They describe their babies as nursing non-stop, and as soon as they take the baby off the breast, they cry frantically. The only time their babies are not crying is when they are breastfeeding. Some mothers say their babies cried while frantically nursing, and nothing consoled them.

Signs of infant hunger.
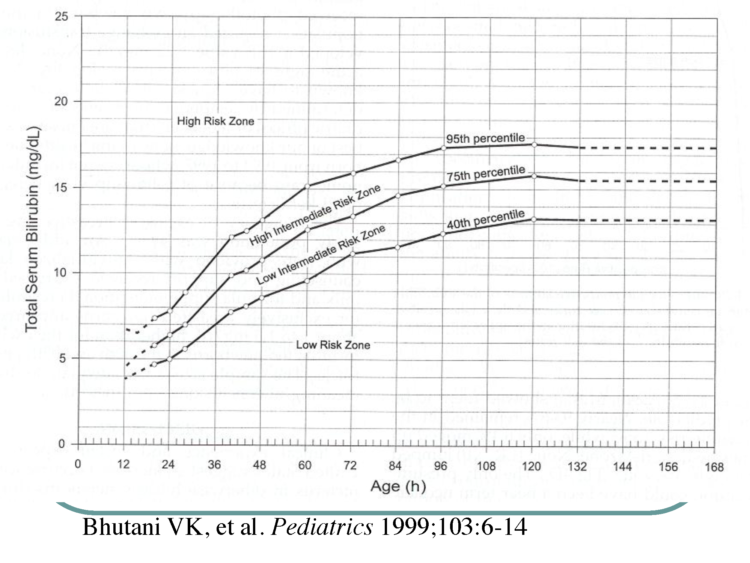
PLEASE know the second night of your baby’s life should never be hell. If your baby is crying non-stop despite adequate breastfeeding, a heel stick check of their glucose (blood sugar), bilirubin, electrolytes, and weight should be performed by a nurse, physician, or nurse practitioner to assess whether a newborn is being sufficiently fed and whether supplementation is needed to protect your newborn from complications of insufficient breastfeeding. *Note: Your baby can be supplemented if you wish to avoid the stress of blood work.
What does research say about colostrum production and milk supply?
Research tells us the delayed onset of full milk production is common, so we cannot ignore the abnormal behavior of a non-stop crying baby, knowing there will be babies who need to be supplemented until the milk supply is adequate.At least 1 in 5 mothers have delayed the onset of full milk production, so we simply cannot ignore the abnormal behavior of a non-stop crying baby,knowing there will be babies who need to be supplemented.

Even Baby-Friendly has admitted that DOL2 is common. BFUSA: “Delayed lactogenesis is actually increasingly common because the risk factors for it are potentially increasing,” Dr. Rosen-Carole
Did you know Bottle-feeding babies do not experience ‘second-night syndrome’
Our ability to see how much milk they consume allows us to provide them with what they need and want. There is no guessing involved.
The good news about temporary supplementation
Studies show supplementation, when necessary, nearly doubles exclusive breastfeeding rates at three months.Preventing breastfeeding complications from inadequate colostrum intake is the ethical and safe thing to do, as no baby should be underfed and forced to cry out in hunger to increase exclusive breastfeeding rates before hospital discharge.
What to expect in the first days home FOR Breastfed Babies
Most breastfeeding families are discharged from the hospital before the arrival of lactogenesis 2 (milk arrival). Mothers have told us they are at home when their baby begins to become very fussy and not satisfied after constant breastfeeding. They panic when they realize their baby needs more than their milk can provide, and they don’t know how to supplement their babyor how toprepare formula safely.
Note: Some babies will be sleepy and lethargic when they do not receive enough colostrum, which is the opposite of a non-stop crying baby. These babies must also be supplemented if they are not feeding well.
If a mother has concerns about her baby not being well-fed, she must call the pediatrician or family physician immediately. You may supplement your baby after nursing sessions, especially if your milk is not enough to keep your baby safely fed. Research has shown that properly managed supplementation to relieve hunger in the first days of life will not impact your breastfeeding relationship and may protect it.More importantly, it can protect your baby from serious complications due to insufficient feeding. It is also recommended for a mother to see her pediatrician the next day after discharge (within 12 hours) from the hospital.
What happens when a newborn hunger cries are ignored?
My Three Day Old Baby Went Limp And Turned Blue; She Was Starving And I Almost Lost Her
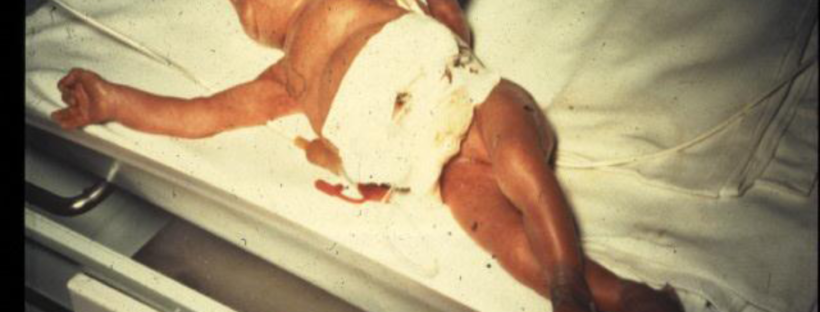
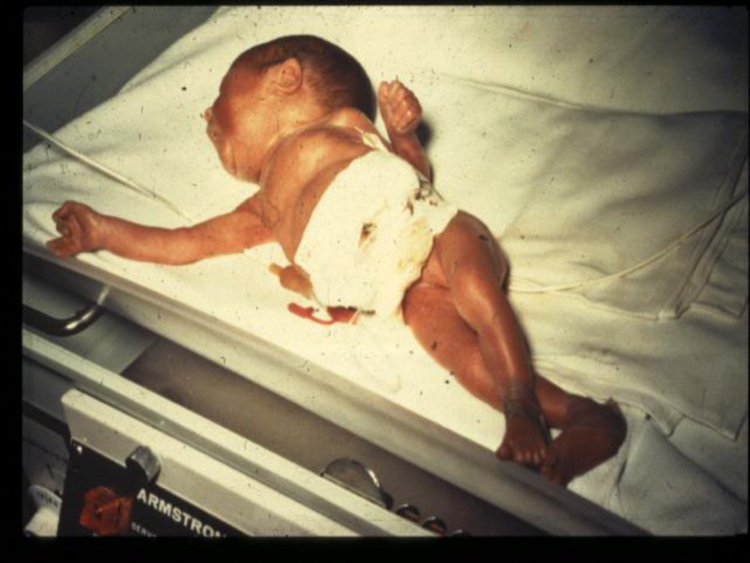
Unfortunately, 1 in 71 exclusively breastfeeding babies are rehospitalized because of insufficient milk intake during the first days of life.
Cluster Feeding
Unfortunately, the phrases “cluster feeding” and “second-night syndrome” are often confused with each other. I wrote about what cluster feeding is and how to know the difference.
Painful nipples from prolonged nursing
Painful, cracked, and bleeding nipples are a serious complication of frequent and prolonged nursing, and sore nipples are one of the top reasons why moms stop nursing. Taking necessary pain medication while in the hospital often masks nipple pain, and when a mom gets home with scabbed bleeding nipples, nursing becomes unbearable. Telling mothers to keep breastfeeding for lengthy periods of time to pacify a hungry baby is the perfect storm for a traumatic and resentful initial breastfeeding experience.
The Take Home Message
It is important to keep breastfeeding a pleasant and gentle experience for both mom and baby. This can be achieved with preparation, flexibility, knowing the difference between a hungry and satisfied baby, and knowing when supplementation may be necessary to protect your baby and your breastfeeding relationship.

Jody Segrave-Daly’s 32-year nursing career has been dedicated to caring for healthy and medically fragile babies in the nursery and NICU. When she began her community-based infant feeding practice ten years ago, she was unprepared to see the significant numbers of babies suffering from accidental starvation complications. The stories she heard were the same –distressed mothers were being told never to supplement their crying, sleepy, jaundiced, and dehydrated babies – or risk ruining their breastfeeding relationship and milk supply. She has comforted countless mothers worldwide who believed it was rare to under-produce breast milk and often felt betrayed by their lactation and healthcare teams, their bodies, and the social pressure that insisted “Breast Is Best.” Now a staunch advocate for the Fed Is Best movement; Jody works to debunk those myths while supporting families to breastfeed, mix-feed, pump-milk-feed, formula-feed, and tube-feed their babies. She uses evidence-based science and her years of clinical experience to support SAFE infant feeding. If you need help, please join our support groupor contact me directly atjody@fedisbest.org
My Baby Scream-Cried The Entire Second Night In The Hospital
How To Prepare For Supplementing When Breastfeeding Your Baby In The Hospital
Feed Your Baby—When Supplementing Saves Breastfeeding and Lives
HOW YOU CAN SUPPORT FED IS BEST
There are many ways you can support the mission of the Fed is Best Foundation. Please consider contributing in the following ways:
- Send us your stories! Share your successes, struggles, and everything in between with us. Every story saves another child from experiencing the same and teaches another mom how to feed her baby safely. Every voice contributes to change. Send to: Jody@fedisbest.org
- Make a donation to the Fed is Best Foundation. We are using funds from donations to cover the cost of our website, our social media ads, and our printing and mailing costs to reach health providers and hospitals. We do not accept donations from breast- or formula-feeding companies, and 100% of your donations go toward these operational costs. All of the Foundation’s work is achieved via its supporters’ pro bono and volunteer work.
- Share the stories and the message of the Fed is Best Foundation through word-of-mouth, by posting on your social media page, and by sending our resources to expectant moms you know. Share the Fed is Best campaign letter with everyone you know.
- Write a letter to your health providers and hospitals about the Fed is Best Foundation. Write them about feeding complications your child may have experienced.
- Print out our letter to obstetric providers and mail it to your local obstetricians, midwives, and family practitioners who provide obstetric care and hospitals.
- Write your local elected officials about what is happening to newborn babies in hospitals and ask for legal protection of newborn babies from underfeeding and for the mother’s rights to honest, informed consent on the risks of insufficient feeding of breastfed babies.7.Send us messages of support. We work daily to make infant feeding safe and supportive of every mother and child. It is your messages of support that keep us all going. The work we do is very emotional and heavy. Thank you!
Thank you so much from the Founders of the Fed is Best Foundation!

Resources and additional education LINKS
How To Prepare For Supplementing When Breastfeeding Your Baby In The Hospital – Fed Is Best
Hospital Drops Baby-Friendly Program After Doctor’s Baby Was Harmed – Fed Is Best
Hospital Drops Baby-Friendly Program After Doctor’s Baby Was Harmed – Fed Is Best
HOW YOU CAN SUPPORT FED IS BEST
There are many ways you can support the mission of the Fed is Best Foundation. Please consider contributing in the following ways:
-
- Join theFed is Best Volunteer groupto help us reach Obstetric Health Providers to advocate for counseling of new mothers on the importance of safe infant feeding.
- Make adonation to the Fed is Best Foundation. We are using funds from donations to cover the cost of our website, our social media ads, and our printing and mailing costs to reach health providers and hospitals. We do not accept donations from breast- or formula-feeding companies, and 100% of your donations go toward these operational costs. All of the Foundation’s work is achieved via its supporters’ pro bono and volunteer work.
- Share the stories and the message of the Fed is Best Foundation through word-of-mouth, by posting on your social media page, and by sending ourresourcesto expectant moms that you know. Share theFed is Best campaign letterwith everyone you know.
- Write a letter to your health providers and hospitals about the Fed is Best Foundation.Write to them about feeding complications your child may have experienced.
- Print out ourletter to obstetric providers and mail them to your local obstetricians, midwives, and family practitioners who provide obstetric care and hospitals.
- Write your local elected officials about what is happening to newborn babies in hospitals and ask for the legal protection of newborn babies from underfeeding and of the mother’s right to honest informed consent on the risks of insufficient breastfeeding of breastfed babies.
- Send us your stories.Share with us your successes, your struggles and everything in between. Every story saves another child from experiencing the same and teaches another mom how to feed her baby safely. Every voice contributes to change.
- Send us messages of support.We work daily to make infant feeding safe and supportive of everymother and child. Your messages of support keep us all going.
Thank you so much from the Founders of the Fed is Best Foundation!