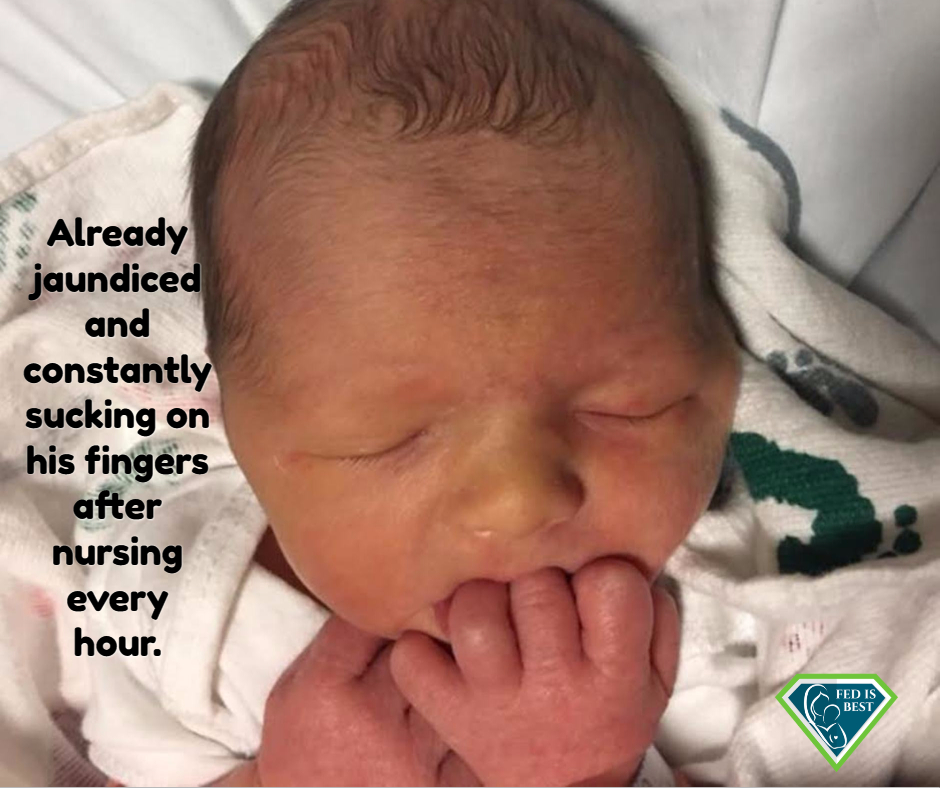
Written by Jody Segrave-Daly, MS, RN, IBCLC
As a veteran NICU, nursery nurse, and lactation consultant, I have cared for and fed thousands of babies over the past 32 years. When working in the special care nursery, babies are fed according to their weight and cumulative losses to determine their caloric requirements for intake amounts and optimal nourishment. For example, term babies admitted to the NICU from complications of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) are immediately fed based on their weight, usually about 60-80 ml/kg/day (typically 15-30 ml) every 2-3 hours. Newborns fed 15-30 ml will likely have their insufficient feeding complications stabilized and demonstrate feeding satisfaction and comfort because the newborn stomach is at least four times larger than what is taught.
First, we should review the anatomy of the newborn digestive system.

Newborn digestive system. Photo credit St. Luke Hospital System, KS
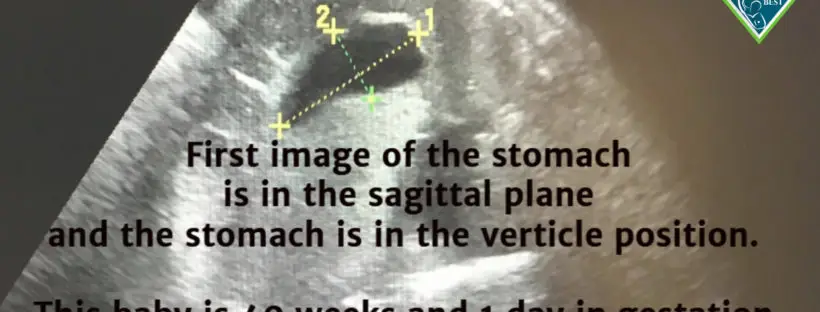
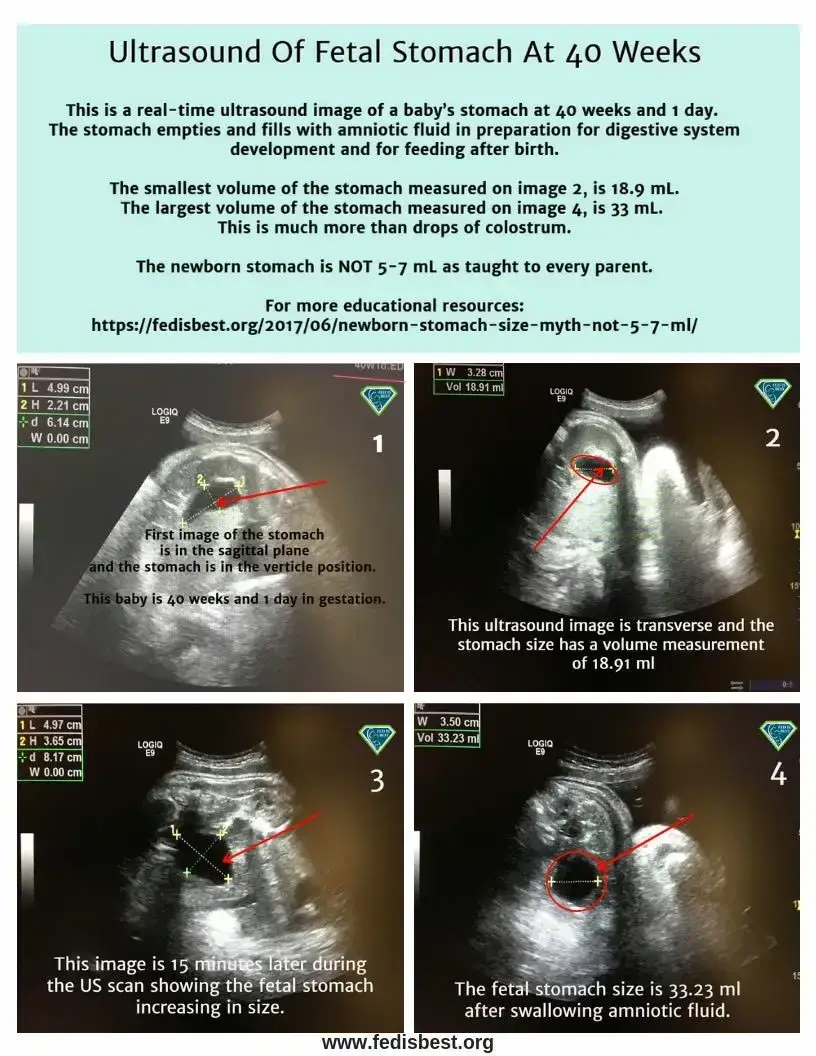
Gastric emptying is a continuous movement into the small intestine, accommodating milk volume of more than 5-7 ml every 2-3 hours. The stomach is a muscular and very stretchable organ. Its biological function is to expand to hold food and fluids while churning with digestive enzymes before entering the duodenum or small intestine. A full-term baby swallows 500-1000 ml of amniotic fluid every day. Ultrasound can confirm the stomach’s size and measure when the baby swallows amniotic fluid. The newborn’s stomach does not magically or suddenly grow after day one, as taught to parents. My concern as a long-time NICU nurse, infant feeding specialist, and IBCLC has always been why mothers are taught their exclusively breastfed newborn baby’s stomach capacity is only 5-7 mL on day one, which is false.

The Myth of the Newborn Stomach Size: Where Did it Come From?
I started my research with my non-clinical hat on and turned to Google since this is where my patients typically go first. When I did a Google search for newborn stomach sizes, there were over 868 thousand links! I was led to a plethora of visual images depicting newborn stomach size. Some of the most popular images were the belly ball models that lactation consultants wear on their lanyards to visually educate new mothers about how big their ‘newborn’s stomach size is.’
I was in absolute disbelief knowing our most trusted lactation consultants were selling, wearing and using, proudly I might say very inaccurate, dangerous and non-evidence based tools that are used in hospitals. I quickly began to understand that ‘belly bead’ models are lucrative merchandise to sell!
With my clinical hat back on, I dug into the science behind these belly balls. In the 2008 Journal of Human Lactation, I found a published article that revealed a completely different utility for belly ball models.
Marble/ball models are often used to represent newborn stomach capacity; however, their accuracy has not been determined:
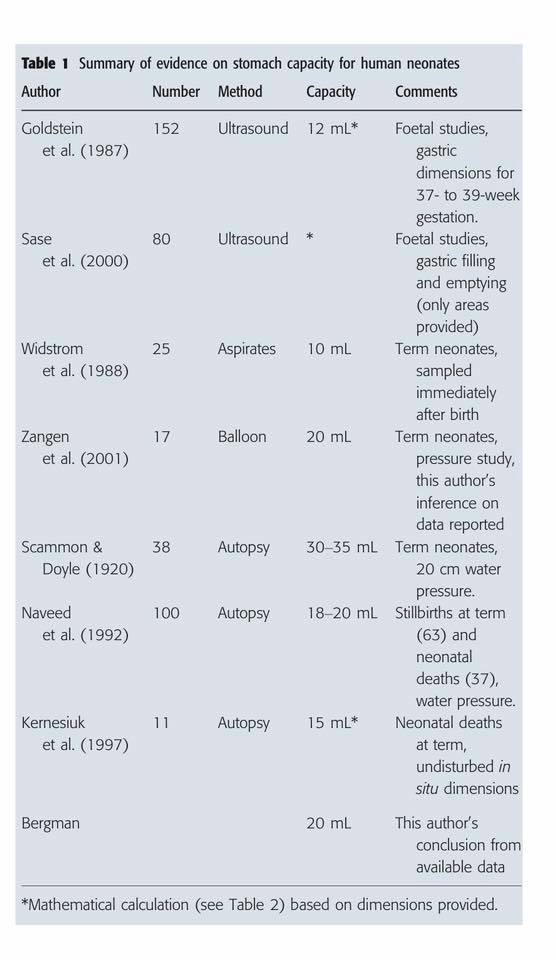
“Measurement of infant stomach capacity has been attempted for over 100 years. Exact volumes cannot be standardized, but data suggest that anatomic and physiologic stomach capacity vary widely.” In addition, “It is important to note that because a wide range of feeding volumes on day one (1-20 mL) and day three (13 to 103 mL) has been reported, and the reasons for these variances are unclear, it may be best to simply acknowledge that feeding volumes vary widely and like stomach capacity, do not lend well to the visual representation given our current knowledge.”
This research was published in 2008 in the Journal of Human Lactation and yet, not a single lactation professional is practicing what the evidence says. How can this be?
New moms are inundated with images of a series of bottles filled with milk depicting the size of an infant’s stomach according to each day after birth, sometimes compared with fruit or different-sized marbles and balls. A mother sent this picture to us, which was in her hospital room after the birth of her baby. She also received inaccurate education about the newborn stomach size and thought her formula-fed baby only needed 5 ml at each feeding.
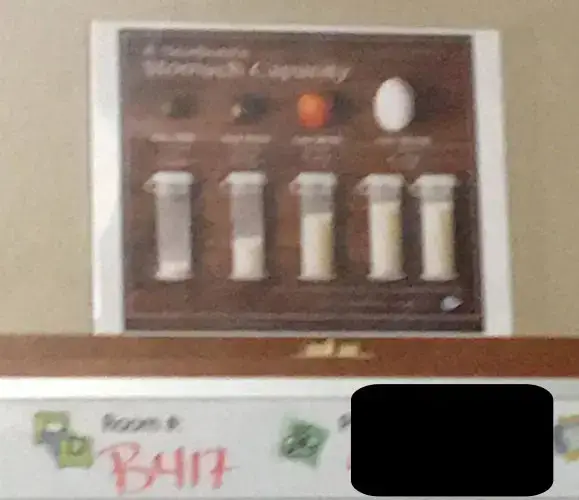

This information is FALSE and based on research from 1920.
I continued to search for more resources, and I found research in 2013 from Consulting Public Health Physician Nils J. Bergman, who published this study, which says:
“There is insufficient evidence on optimal neonatal feeding intervals, with a wide range of practices. The stomach capacity could determine feeding frequency. A literature search was conducted for studies reporting volumes or dimensions of stomach capacity before or after birth. Six articles were found, suggesting a stomach capacity of 20 ml at birth.”

Dr. Bergman states, “There is reasonable consensus on the amount of milk that human term newborn infants need per day; figures given vary from 150 to 160 mL/kg/day.”
This means an average 3 kg or 6.6 lb newborn requires 450-480 mL or 16 ounces of milk daily. At 66 Calories/dL, this would roughly be 100-106 Cal/kg/day, which is the published daily caloric requirement for a newborn. This total volume can be given in smaller volumes more frequently or larger volumes less frequently, 2 ounces every 3 hours or 1.3 ounces every 2 hours.
His article poses the hypothesis that the feeding interval should be 20 mL every 1 hour, assuming that every mother produces 20 ml of colostrum every hour.
However, the real-life hypothetical clinical application of his suggested feeding interval would quickly lead to maternal and newborn exhaustion from lack of sleep and increased risk of postnatal depression, breastfeeding cessation, and even suffocation from a mother falling asleep with her newborn during breastfeeding. In addition, his feeding interval does not consider that the stomach actually empties during feeding; therefore, a newborn’s feeding capacity is higher than 20 mL. The clinical expertise of neonatal health professionals has shown that even one-day-old newborns are able and do comfortably tolerate 15-30 MLS per feeding every 2-3 hours.
Additional newborn stomach size research

The most popular breastfeeding education resources for new parents also refer to false information by teaching that the stomach size is 5-7 ml on day one. This picture is from a mother who delivered in a Baby-Friendly Hospital this week. Imagine her confusion when her baby required 30 mL of supplemental milk to treat hypoglycemia.

No one could explain to her why her baby could comfortably tolerate more milk than what she was taught in this hospital education resource booklet.
Dr. Gomez, a neonatologist, explains why hypoglycemic babies (low blood sugar) need more than 5 ml of milk despite being told their baby’s stomach can only hold 5 ml.
“We don’t have any strong evidence as to the size of the stomach for each baby. However, we do have significant scientific evidence that hypoglycemia and under-hydration cause damage to the brain of the infant.
We have solid evidence that feeding babies 10-20 mls when they are born is adequate to keep the blood glucose levels up in most babies. Some will still need some other interventions, but 10- 20 ml feedings are enough most of the time.
There is no evidence that feeding 10 to 20 ml of milk to a baby causes “stretching of the stomach,” and we don’t have ANY evidence that this is detrimental to the baby.”
We have evidence that judicious supplementation helps babies and does not impact breastfeeding rates.
So the question is, are we hurting babies by supplementing? NO. Are we hurting babies by not supplementing and allowing them to have hypoglycemia or dehydration? YES.
According to the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine Supplementation Protocol, they suggest exclusively breastfed babies are fed 2-10 ml per feeding, and they reference the infant’s stomach size according to outdated studies (1992 and 1920) to reflect intake volume. They also say there is no definitive research available, and the amount of supplement given should reflect the normal amounts of colostrum available, the size of the infant’s stomach, and the age and size of the infant.
Unfortunately, this information contributes to additional confusion that already exists for parents. What they do say is research is necessary to establish evidence-based guidelines on appropriate supplementation volumes for specific conditions and whether this varies for colostrum versus infant formula.
But why don’t we already know this if an infant feeding protocol has been implemented in hospitals? Protocols are supposed to be peer-reviewed for scientific accuracy.
Speaking of HUNGER cues and feeding your baby to satisfaction, here are signs that your newborn baby needs immediate attention:

We have been talking about the newborn stomach size, but what about calories? How many calories do human milk, infant formula, and colostrum contain in 5-7 MLS?
What research tells us is :
- Mature breast milk averages around 20 calories per ounce (~30 mL)
- and infant formula contains 20 calories per ounce as well.
- Colostrum is lower in fat and carbohydrates and comes in at around 17 calories per ounce (~30ml) (Guthrie 1989).

How many calories do term newborns need to ensure Cell Survival?

As you can see, exclusively breastfed newborns cannot thrive on three calories per 5 ml (1 teaspoon) of colostrum at each feeding.

Some exclusively breastfed babies are fasting after birth if they are not receiving enough colostrum. 1 in 5 new mothers can experience delayed onset of copious milk production due to various risk factors. This puts these babies at risk for developing complications from insufficient colostrum intake while breastfeeding.
1 in 71 exclusively breastfed babies are rehospitalized for life-threatening complications from insufficient colostrum intake. As lactation and neonatal medicine professionals it is imperative to update our educational resources and identify the babies who may need timely supplementation before the onset of copious milk production. For mothers who desire to exclusively breastfed, donor milk should be made available for them to use if supplementation is needed. In order for babies to receive the full benefits of breastfeeding, they need to be safely fed at every feeding.
So, how often should exclusively breastfed babies eat?
There is no single correct answer to this question because each baby has a different weight and unique caloric requirement. Babies should be fed according to their hunger cues and to satisfaction, along with other clinical observations such as excessive weight loss, low blood sugar, excessive jaundice, or dehydration. We have a feeding plan that you can follow to determine how well your baby is feeding. (currently being updated.)
If your baby is crying and crying after breastfeeding, an immediate medical exam is necessary to be sure the baby is not suffering from insufficient intake of colostrum while exclusively breastfeeding. If a medical evaluation is not immediately available, especially before the milk has come in, supplementation may be urgently needed to feed your hungry baby before medical evaluation is available to prevent serious complications of insufficient feeding.
A mother writes: “Because of this stupid belly bead, my baby was discharged from the hospital despite not eating enough breastmilk. He had a seizure at home and was taken back to the hospital by an ambulance for dehydration.”

As you can see, It’s time to ban the false belly bead models and update our breastfeeding education resources immediately. Our babies are counting on us to keep them well-fed, meeting their metabolic needs with sufficient milk, and using the best and most current infant feeding practices possible. Too many babies are being harmed by this flawed product.
Was your baby harmed by the belly bead lanyard product?

Normal Newborn Anatomy and Function | High Impact® Visual Litigation Strategies™
(Blog Updated February 6, 2022)

Jody Segrave-Daly’s 32-year nursing career has been dedicated to caring for healthy and medically fragile babies in the nursery and NICU. When she began her community-based infant feeding practice 12 years ago, she was unprepared to see the significant numbers of babies suffering from accidental starvation complications. The stories she heard were the same —distressed mothers were being told never to supplement their crying, sleepy, jaundiced, and dehydrated babies — or risk ruining their breastfeeding relationship and milk supply. She has comforted countless mothers worldwide who believed it was rare to under-produce breast milk and often felt betrayed by their lactation and healthcare teams, their bodies, and the social pressure that insisted “Breast Is Best.” Now a staunch advocate for the Fed Is Best movement, Jody works to debunk those myths while supporting families to breastfeed, mix-feed, pump-milk-feed, formula-feed and tube-feed their babies. She uses evidence-based science and her years of clinical experience to support SAFE infant feeding. She also prioritizes perinatal mental health when counseling parents about their feeding options. Ultimately, every family has different needs and deserves individualized, unbiased, inclusive, and shame-free support. If you need help, please join our support group or contact her directly at [email protected]. If you need infant feeding support, we have a private support group– Join us here.

Are you a healthcare professional and want to join our advocacy? Click here to join us!
If I Had Given Him Just One Bottle, He Would Be Alive.
WE ARE EXCITED TO ANNOUNCE OUR UPCOMING BOOK!
It is now available for pre-order at all major retailers! Coming June 25, 2024!
Go to Fed is Best Book to pre-order today!
FAQs Part 2: Does The Fed Is Best Foundation Believe All Exclusively Breastfed Babies Need Supplementation?
Baby-Friendly USA Acknowledges Their Mistakes; Are They Going To Make Real Changes In The New Year Or Are They Providing Lip Service To Mothers?
Additional research about the newborn stomach size:
The Pediatric Surgery Journal describes the newborn stomach anatomy, including the size of 30 ml at birth:

Pediatric Anatomy Surgery Journal
Normal third-trimester fetal anatomy -ultrasound videos: the abdomen:
Guthrie, Helen Andrews. Introductory Nutrition. St. Louis : Times Mirror/Mosby College Pub., 1989
Breastfeeding confidence and measurement of milk intake
Newborn feeding recommendations and practices
The American Academy of Pediatrics’ Breastfeeding Guidelines
Helpful guide to safe infant feeding amounts from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Helpful overview of infant feeding for the first month of life, from the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Feed Your Baby—When Supplementing Saves Breastfeeding and Lives
Normal Human Lactation; closing the gap
HOW YOU CAN SUPPORT FED IS BEST
There are many ways you can support the mission of the Fed is Best Foundation. Please consider contributing in the following ways:
- Send us your stories. Share with us your successes, your struggles, and everything in between. Every story saves another child from experiencing the same and teaches another mom how to feed her baby safely. Every voice contributes to change.
- If you need infant feeding support, we have a private support group– Join us here.
- If you or your baby were harmed from complications of insufficient breastfeeding, please send a message to [email protected]
- Make a donation to the Fed is Best Foundation. We are using funds from donations to cover the cost of our website, our social media ads, and our printing and mailing costs to reach health providers and hospitals. We do not accept donations from breast- or formula-feeding companies, and 100% of your donations go toward these operational costs. All of the Foundation’s work is achieved via its supporters’ pro bono and volunteer work.
- Share the stories and the message of the Fed is Best Foundation through word-of-mouth, by posting on your social media page and by sending our FREE infant feeding educational resources to expectant moms you know. Share the Fed is Best campaign letter with everyone you know.
- Write a letter to your health providers and hospitals about the Fed is Best Foundation. Write to them about feeding complications your child may have experienced.
- Print out our letter to obstetric providers and mail it to your local obstetricians, midwives, and family practitioners who provide obstetric care and hospitals.
- Write your local elected officials about what is happening to newborn babies in hospitals and ask for the legal protection of newborn babies from underfeeding and for the mother’s rights to honest, informed consent on the risks of insufficient feeding of breastfed babies.
- Join us in any Fed is Best volunteer and advocacy groups. Click here to join our group of healthcare professionals. We have: FIBF Advocacy Group, Research Group, Volunteer Group, Editing Group, Social Media Group, Legal Group, Marketing Group, Perinatal Mental Health Advocacy Group, Private Infant Feeding Support Group, Global Advocacy Group, and Fundraising Group. Please email [email protected] if you want to join any of our volunteer groups.
- Send us messages of support. We work daily to make infant feeding safe and supportive of every parent and child. Your messages of support keep us all going.
Donate to Fed is Best
Thank you so much from the Founders of the Fed is Best Foundation!
Jody and Christie